Ginkgo biloba L. leaf extract is a safe option in elderly population
Objective
The objective of this study was to evaluate clinical and genomics safety of Ginkgo biloba L. leaf extract in elderly population
Methods and study design
This was a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study conducted in elderly subjects. A total of 140 elderly subjects, aged 65 years or more were enrolled in this study. However, 74 subjects did not meet the eligibility criteria; only 66 subjects (26 males and 40 females) participated in this study. Subjects randomly received either Ginkgo biloba L. leaf extract (120 mg) or placebo twice a day for 6 months. Clinical condition of all patients was monitored at the beginning, during and after treatment.
Results
- No adverse effects were reported due to Gingko biloba treatment
- Gingko biloba treatment did not
- result in any adverse clinical symptoms
- cause any liver injury
- cause any genomic instability and DNA damage
- cause altered expression of liver cancer genes
Conclusion
Based on the observations of this study, the researchers opine that Ginkgo biloba L. leaf extract does not have a potential to increase risk of any adverse effects. Ginkgo biloba could be a safe option for the elderly population.
Source
Bonassi S, Prinzi G, Lamonaca P, et al. Clinical and genomic safety of treatment with Ginkgo biloba L. leaf extract (IDN 5933/Ginkgoselect® Plus) in elderly: a randomised placebo-controlled clinical trial [GiBiEx]. BMC complementary and alternative medicine. 2018;18(1):22.
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in brain development
Objective
The objective of this study was to evaluate the role of DHA in brain development.
Methods and study design
This was a review article written by Echeverría F et al and intends to review the current information on docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a fundamental fatty acid for the brain. The authors have reviewed the studies that support the importance of DHA for humans especially in brain development and neuroprotection.
Results
The key observations of the studies reviewed by the researchers is summarized under the following headers
- DHA and human evolution
- The initial data on the importance of DHA on the growth and physiology of the central nervous system (CNS) comes from the fossils
- The data indicate that the early humans consumed seafood—fish, shellfish, and algae that are rich on n-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFA) mainly eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and DHA
- DHA in brain development
- DHA is the most abundant n-3 LCPUFA in the brain, peripheral nervous system and the retina
- DHA is responsible for the fetal brain development and results in better visual development, retinal and visual maturation
- DHA supplementation improves punctuation for vocabulary and comprehension tests
- DHA in neuroprotection
- DHA is the fundamental unit for neuronal structure and signaling
- Increased level of blood DHA reduces 47% of risk of Alzheimer’s disease
- DHA supplements increases the plasma level of transthyretin which in turn reduces the accumulation of toxic peptides in brain
- DHA shows significant increase in cognitive and memory skills associated with brain blood flow
- Daily consumption of DHA and lutein showed a significant improvement in memory and learning in 60-80 years old women
- Supplementation with DHA showed a protective effect against hypoxia-ischemic brain injury, reduces oxidative damage at 24 hours and 8 weeks after brain injury
Conclusion
Based on observation of this study, the researchers opine that daily intake of DHA improves brain development and has neuroprotective benefits
Source
Echeverría F, Valenzuela R, Hernandez-Rodas MC, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a fundamental fatty acid for the brain: New dietary sources. Prostaglandins, Leukotriene’s and Essential Fatty Acids. 2017;124:1-0.
Effect of docosahexaenoic acid on cognitive function and mental health
Objective
The objective of this study was to evaluate effect of DHA enriched meal on cognitive function in elderly population
Methods and study design
This was a randomized, double –blind, placebo controlled study conducted in elderly subjects .A total 84 elderly subjects aged 75 years or more were enrolled in this study. However 9 subjects did not meet the eligibility criteria, only 75 subjects (10 male and 65 females) participated in this study. Subjects randomly received either family style meal that include fish sausages containing 860 mg DHA, 203 mg EPA or placebo for 12 months.
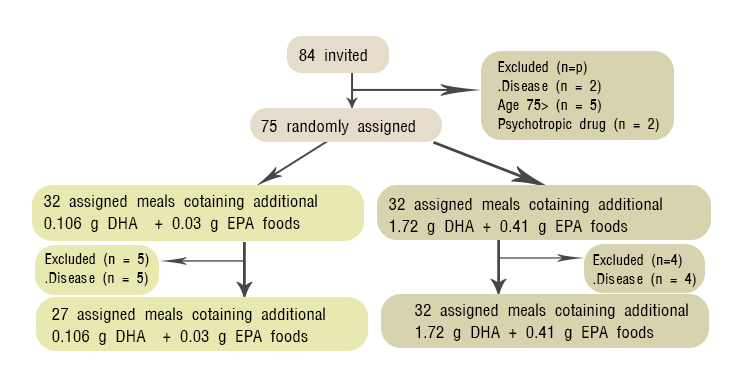
Results
The key observations of the studies reviewed by the researchers are summarized under the following headers
- DHA in nutritional intake: DHA enriched meals for 12 months did not show any side-effects in elderly patients.
- DHA in cognitive functions
- Increased level of plasma n-3 PUFA reduces risk of development of dementia
- Daily consumption of DHA shows signicficant protection against age related cognitive problems in oldest-elderly people
- Dietary supplementation with n-3 PUFA increases dopamine level and D2 receptors which helps to reduce the risk of development of dementia
- Supplementation with DHA and ETA (1.3 g/day and 0.45g/day) showed a significant effect on short-term memory,verbal memory,working memory and delayed recall capability.
Conclusion
Based on observation of this study, the researchers opine that long term usage of dietary enriched meal with DHA improves age-related cognitive function and mental health in elderly subjects.
Source
Hashimoto M, Kato S, Tanabe Y,et al.Beneficial effects of dietary docosahexaenoic acid intervention on cognitive function and mental health of the oldest elderly in Japanese care facilities and nursing homes. Geriatrics & gerontology international. 2017;17(2):330-7.
Docosahexaenoic Acid Supplementation in Alzheimer Disease
Objective
The objective of this study was to evaluate an association of docosahexaenoic acid supplementation in Alzheimer’s disease.
Methods and study design
This was a review article written by Hussein N et al and intends to review the current information on an association of docosahexaenoic acid supplementation with Alzheimer’s disease stage in Apo lipoprotein E ε4 carriers.The authors reviewed the studies that support the importance of DHA in Alzheimer’s disease.
Results
- Omega-3 intake in cognitive outcomes
- The data indicates that higher level of saefoods-fish,algae that are rich on Omega -3 fatty acids mainly DHA and EPA ignificantly reduces the incidence of AD.
- Supplementation with Omega-3 fatty acids significantly improves episodic memory.
- DHA in APOE genotype
High intake of omega-3 fatty acids or seafoods per week showed significant reducation in AD neuropathological changes in APOE4 individuals.
Conclusion
Based on observation of this study, the researchers opine that DHA supplementation in APOE4 have potential beneficial effect in dementia.
Source
Yassine HN, Braskie MN, Mack WJ, et al. Association of docosahexaenoic acid supplementation with Alzheimer disease stage in Apo lipoprotein E ε4 carriers: a review. JAMA neurology. 2017;74(3):339-47.
DHA Prevents the Extraggression of Mental status
Objective
DHA is found in the phospholipid fraction of the brain and is a major polyunsaturated fatty acid of the brain .It was not known whether supplemental DHA has any effects on the higher functions of the brain in young adults. So, this study was conducted to assess the efficacy of DHA in preventing aggression in adults.
Study design
A placebo-controlled double-blind study.
Number of subjects
41 young adults.
Study intervention
1.5-1.8 g of DHA daily (n =22) or control oil (n =19).
Duration of the study
3 months
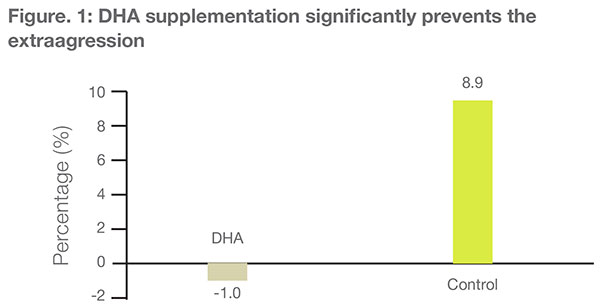
The stability in extraggression percentage in the DHA group indicates aggression-controlling effects of DHA
Results
- DHA therapy caused significant alterations in the extraggression (aggression against others) in comparison to the placebo group, where it was significantly increased (see Fig. 1) (p=0.0029).
- The 95% CI difference between the DHA and control groups were found to be -16.8% to -3.0%, respectively.
Conclusion
DHA supplementation significantly prevents extraggression in young adults
Source
Hamazaki T, Sawazaki S, Itomura M, et al. The effect of docosahexaenoic acid on aggression in young adults. A placebo-controlled double-blind study. J Clin Invest. 1996;97(4):1129-1133