A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled parallel study was conducted by Kelley, et al. to assess the effects of DHA supplementation on the concentrations of apoproteins, large, medium and small VLDL, LDL, and HDL particles and the mean diameters of these particles in fasting and postprandial plasma.
4 hypertriglyceridemic patients aged 39-66 years
3 months
Patients received no supplements for the first 8 days and then received either 7.5 g DHA oil/day (3 g DHA/day) obtained from microalgae Crypthecodinium cohinii or 7.5 g olive oil (placebo group) for the last 90 days
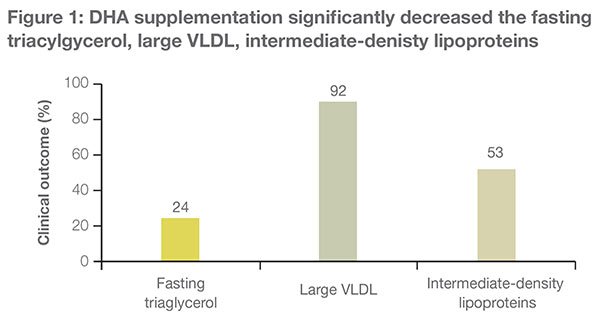
DHA supplementation for 45 days significantly (P<0.05) decreased concentrations of fasting triacylglycerol, large VLDL, and intermediate-density lipoproteins and the mean diameter of VLDL particles.
DHA supplementation for 45 days (mid intervention) resulted in a 92% decrease in the concentrations of large VLDL particles and a 133% increase in the concentrations of small VLDL particles.
DHA supplementation decreased the concentration of intermediate LDL particles by 53% and increased those of large LDL particles by 120%.
DHA supplementation for 45 days significantly reduced heart rate (8.3%) and systolic (5.6%) and diastolic (4.0%) blood pressures compared with baseline.
DHA supplementation reduced the concentrations of atherogenic lipids and lipoproteins and increased concentrations of cardio-protective lipoproteins
Mori TA, Bao DQ, Burke V, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid but not eicosapentaenoic acid lowers ambulatory blood pressure and heart rate in humans. Hypertension. 1999;34(2):253-260