The consumption of omega-3 fatty acids is associated with decreased risk of fatal myocardial infarction. However, the effect of the docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) on vascular function was unknown.
Therefore, this study was conducted to assess the efficacy of algal DHA on vascular function.
Significant increase in the proportion of DHA in erythrocytes lipids by 58% in comparison with placebo treatment.
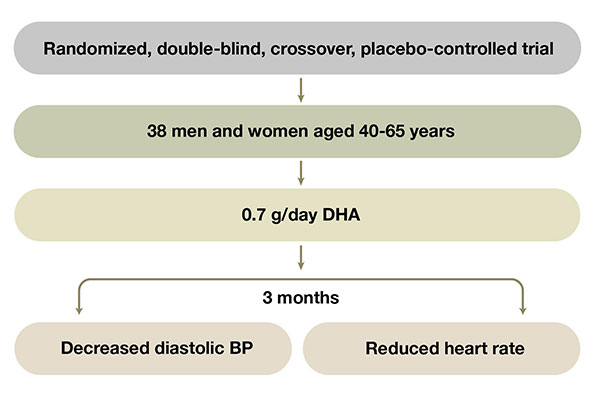
The diastolic blood pressure (DBP) was found to be significantly decreased by 3.3 mm Hg (95% confidence interval {CI} -6.1 to -0.6; p =0.01) in comparison to placebo.
Furthermore, the heart rate was also found to be reduced by 2.1 beats/min in DHA supplemented group in comparison to the placebo group (p=0.15).
In conclusion the authors of the study revealed that the moderate increase in the daily intake of DHA is associated with lowering of diastolic BP, however, short term DHA supplementation did not show any positive association in endothelial function or arterial stiffness.
Theobald HE, Goodall AH, Sattar N, et al. Low-dose docosahexaenoic acid lowers diastolic blood pressure in middle-aged men and women. J Nutr. 2007;137(4):973-978.